Basic Research & Development Flow Chart.
R&D may take months or years to yield fruitful results. Though each company or industry may have its own unique research methodology, a basic research process forms the framework for it.
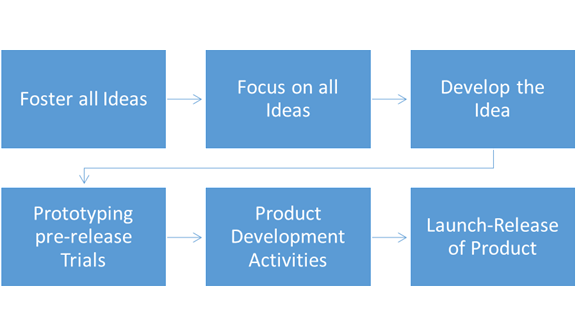
Foster Ideas
At this point the Engineering team sits down to brainstorm. The discussions will start with an understanding of the scope of work and itemization of a particular issued faced and then narrowed down to the important core areas of opportunity or concern.
Focus Ideas
The initial pool of ideas is vast and may be generic. The Engineering team will then sift through these and locate ideas with potential or those that do not have insurmountable limitations. At this point the team may look into an existing product and assess how original a new idea is and how well it can be developed.
Develop Ideas
Once the idea has been researched and been developed it may be assessed for market readiness. Ideas with true potential and the process of turning research into a marketable commodity begins.
Prototypes and Trials
The Engineering team works closely with Marketing to understand and agree on how an idea may turn into a practical product. As the process iterates, the prototype complexity may start to increase and issues such as mass production and sales tactics may begin to enter the process.
Regulatory, Marketing & Product Development Activities
As the product takes shape, the process that began with R&D divides into relevant areas necessary to bring the research product to the market. Regulatory aspects are being assessed and work begins to meet all the criteria for approvals and launch. The marketing and sales function begins to develop strategies and preparation of materials while sales, pricing and distribution are also planned for.
Launch
The product that started as a research question will now be ready for its biggest test, the introduction to the market. The evaluation of the product continues at this stage and beyond, eventually leading to possible re-designs if needed.
A very important factor along the launch is that at any point in this process the idea may be abandoned. Its feasibility may be questioned, or the research may not reveal what the business hoped for at the end of the day. It is therefore important to analyse each idea critically at every stage and not become emotionally invested in anything.
